What is Composition of Kraft Paper?
Kraft paper, known for its strength, durability and versatility, is a highly popular paper product used in various applications from packaging to art projects. But what exactly makes Kraft paper so resilient and eco-friendly?
Understanding its composition not only reveals the factors contributing to its sturdiness but also explains its environmental advantages. In this article, we’ll explore Kraft paper’s components, manufacturing process, types and how it stands out in the world of paper products.
Understanding Basics of Kraft Paper Composition
Kraft paper is primarily composed of chemical pulp produced through the Kraft process, which involves converting wood into wood pulp that is rich in cellulose.
This process utilizes a strong alkaline solution containing sodium hydroxide and sodium sulfide to break down the wood chips and separate the fibers.
This results in a pulp that retains more lignin than conventional paper, contributing to its strength and durability. Additionally, the brown color of natural Kraft paper is due to the presence of lignin and other wood fibers, although it can undergo bleaching if a lighter appearance is desired.
Unbleached version is more environmentally friendly as it involves fewer chemicals and retains more of the wood’s natural properties. The combination of chemical processes and minimal breakdown of fibers makes Kraft paper notably resilient and a top choice for robust packaging solutions.
Composition of Kraft Paper
- Wood pulp: Kraft paper is primarily composed of wood pulp, specifically from long fibers of pine trees. These long fibers contribute to the strength and durability of Kraft paper, making it suitable for heavy-duty applications such as packaging.
- Sulfate process: Manufacturing process of Kraft paper involves a chemical pulping method known as the sulfate or Kraft process. Unlike other types of paper, this process does not involve bleaching the wood pulp, resulting in a natural brown color unique to Kraft paper.
- Chemicals: Chemicals such as sodium hydroxide and sodium sulfide are used in the sulfate process to break down the lignin in wood pulp, which binds the fibers together. This results in stronger and more resilient paper.
- Water: Large amounts of water are also used in the manufacturing process of Kraft paper, making it a resource-intensive product. However, many Kraft paper manufacturers have implemented sustainable practices to reduce their water consumption and environmental impact.
- Additives: In addition to wood pulp and chemicals, Kraft paper may also contain additives such as starch, resin, or wax for added strength and moisture resistance. These additives are biodegradable and do not affect the overall eco-friendliness of Kraft paper.
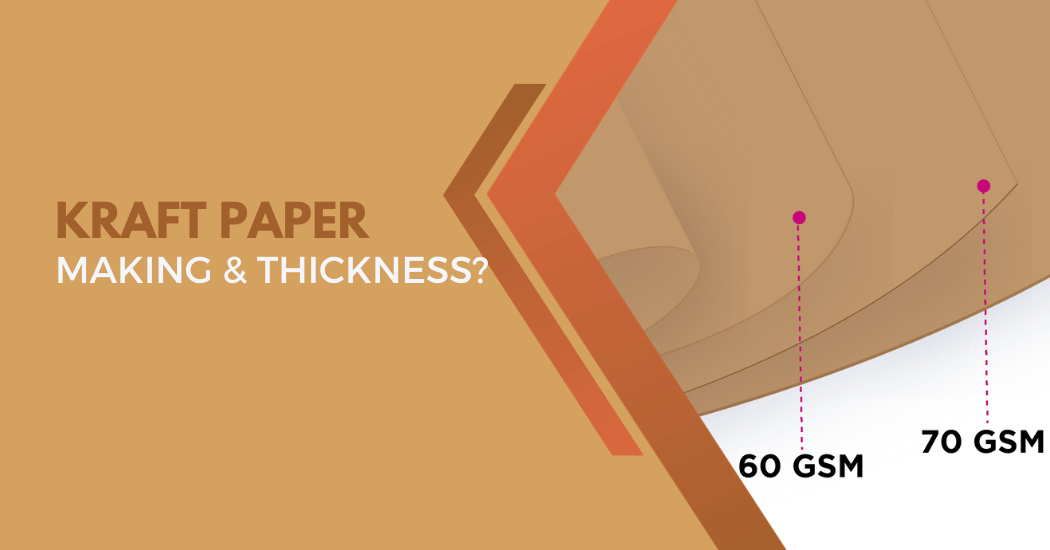
The Kraft Process: How Kraft Paper is Made?
- Pulping: Kraft process begins with the pulping stage, where wood chips are mixed with a cooking liquor consisting of sodium hydroxide and sodium sulfide. This mixture is heated under pressure in a digester to break down the lignin and free the cellulose fibers.
- Washing: After cooking, the pulp is washed to remove the residual chemicals and lignin. This results in a strong, brown pulp that is characteristic of Kraft paper.
- Screening: Washed pulp is then screened to remove any remaining impurities or large fiber bundles that could affect the quality of kraft paper.
- Beating and refining: Next pulp undergoes a beating and refining process that improves fiber bonding and enhances the paper’s strength and texture. Additives can also be introduced at this stage to impart specific qualities, such as water resistance or a smoother finish.
- Paper formation: Refined pulp is diluted with water and spread onto a moving mesh screen, where it forms a continuous sheet. Water drains away, leaving behind a wet paper web.
- Pressing and drying: Wet paper web is passed through a series of rollers to press out excess water and increase fiber bonding. It is then dried by heated cylinders, solidifying the paper structure.
- Finishing: Finally, Kraft paper is finished according to its intended use. This may involve cutting, coating or printing to meet specific requirements. Finished product emerges as a resilient, eco-friendly material capable of fulfilling diverse demands across industries.
Types of Kraft Paper
- Natural Kraft paper: This is the most commonly used type of Kraft paper and has a natural brown color due to the sulfate process. It is available in various thicknesses and can be further enhanced with additives for specific purposes.
- Bleached Kraft paper: Unlike natural Kraft paper, this type undergoes a bleaching process that results in a white or cream-colored product. It is often used for packaging delicate items or as a base for printing.
- Colored Kraft paper: Colored pigments can be added during the manufacturing process to produce different shades of Kraft paper, making it suitable for decorative projects or adding visual appeal to packaging.
- Recycled Kraft paper: As the name suggests, this type of Kraft paper is made from recycled materials, promoting recycling and making it an even more environmentally friendly option.
Comparison with Other Paper Types
| Feature | Kraft Paper | Cardboard | Recycled Paper |
|---|---|---|---|
| Manufacturing Process | Chemical pulping via sulfate process | Compressed paper fibers bonded together | Collected, processed and remade into new paper |
| Color | Natural brown, bleached white or colored | Typically brown or gray | Varied, usually with a duller finish |
| Strength | High due to long fibers and sulfate process | Moderate to high, depending on thickness | Moderate but improved through fiber regain |
| Uses | Packaging, wrapping, crafts, envelopes | Boxes, packaging, shipping containers | Printing, writing, notepads, tissues |
| Environmentally Friendly | Yes, especially unbleached and recycled versions | Depends on sourcing and recycling methods | Yes, by using post-consumer materials |
| Additives | Possible starch, resin or wax for strength/moisture resistance | Alkaline sizing and surface treatments | Dependent on end use requirements |
| Recyclability | Highly recyclable, especially unbleached | Recyclable but with less fiber quality recycle | Typically recyclable with proper sorting |
Understanding the distinct characteristics of each paper type helps industries choose the most suitable material for their needs.
While Kraft paper is celebrated for its durability and eco-friendliness, cardboard provides structural robustness ideal for heavy-duty uses.
How to Choose the Right Kraft Paper Based on Composition?
Here are some factors to consider when choosing Kraft paper based on its composition:
- Fiber length: Longer fibers in Kraft paper result in a stronger and more durable product, making it suitable for packaging and heavy-duty applications.
- Burst strength: This measures the amount of pressure needed to burst a specific area of paper. Higher burst strength is desirable for packaging purposes.
- Additives: Depending on the intended use, additives such as starch, resin or wax can be added during the manufacturing process to enhance specific properties of the Kraft paper.
- Recycled content: For those looking for a more sustainable option, choosing Kraft paper made from a high percentage of recycled materials is recommended.
- Coating or finish: Type of coating or finish applied to Kraft paper can also affect its performance and suitability for different applications. A smooth finish may be better for printing, while a rougher finish may provide more grip and cushioning for packaging.
- Grammage (basis weight): This refers to the weight of paper per unit area and is an important consideration for determining the strength and thickness of the Kraft paper needed.
- Color: As mentioned earlier, Kraft paper comes in various colors, each with its unique properties. For example, natural Kraft paper has better strength and tear resistance compared to bleached Kraft paper.
- Intended use: Ultimately, the choice of Kraft paper should depend on its intended use. Consider factors such as strength requirements, environmental impact and visual appeal when selecting the right composition for your needs.
Overall, understanding the composition of Kraft paper can help businesses choose the most suitable type for their specific needs, whether it be for packaging, printing or other applications.
Applications of Kraft Paper
Kraft paper is a versatile material with a wide range of applications across various industries. Its strength, durability and eco-friendliness make it a popular choice for many purposes:
- Packaging and Shipping: Kraft paper is commonly used for packaging and wrapping products due to its high tensile strength, which protects items during transit. It is also frequently used as a protective liner in boxes and shipping containers.
- Crafting and Art Projects: Artists and crafters value Kraft paper for its natural texture and aesthetic appeal. It serves as an excellent medium for drawing, painting and other creative projects. Its rigidity also makes it suitable for creating sturdy craft items.
- Retail and Branding: Many retailers use Kraft paper bags as a sustainable packaging solution. The ability to print logos and designs on Kraft paper enhances brand visibility and reinforces eco-conscious branding messages.
- Food Industry: Kraft paper is often used in the food industry for wrapping food items, especially baked goods. Its non-toxic properties and ability to maintain freshness make it a reliable material for food packaging.
- Gardening and Landscaping: In landscaping, Kraft paper functions as a biodegradable weed barrier and mulch. Additionally, it’s used in crafts for making seed pots and other gardening solutions that minimize environmental impact.
Each application benefits from the inherent properties of Kraft paper, allowing industries to leverage its strengths for specific needs, from enhancing product protection to promoting sustainability goals.
Final Words
Kraft paper stands out as a remarkable material due to its versatility, strength and environmental benefits. Its unique composition makes it suitable for a wide array of applications, from industrial uses like packaging and shipping to creative projects and sustainable branding.
By understanding its distinct characteristics and choosing the right type of Kraft paper for specific purposes, businesses and individuals can harness its full potential while contributing to eco-friendly initiatives.
As the demand for sustainable solutions grows, Kraft’s paper’s relevance remains significant in supporting a more environmentally conscious future.